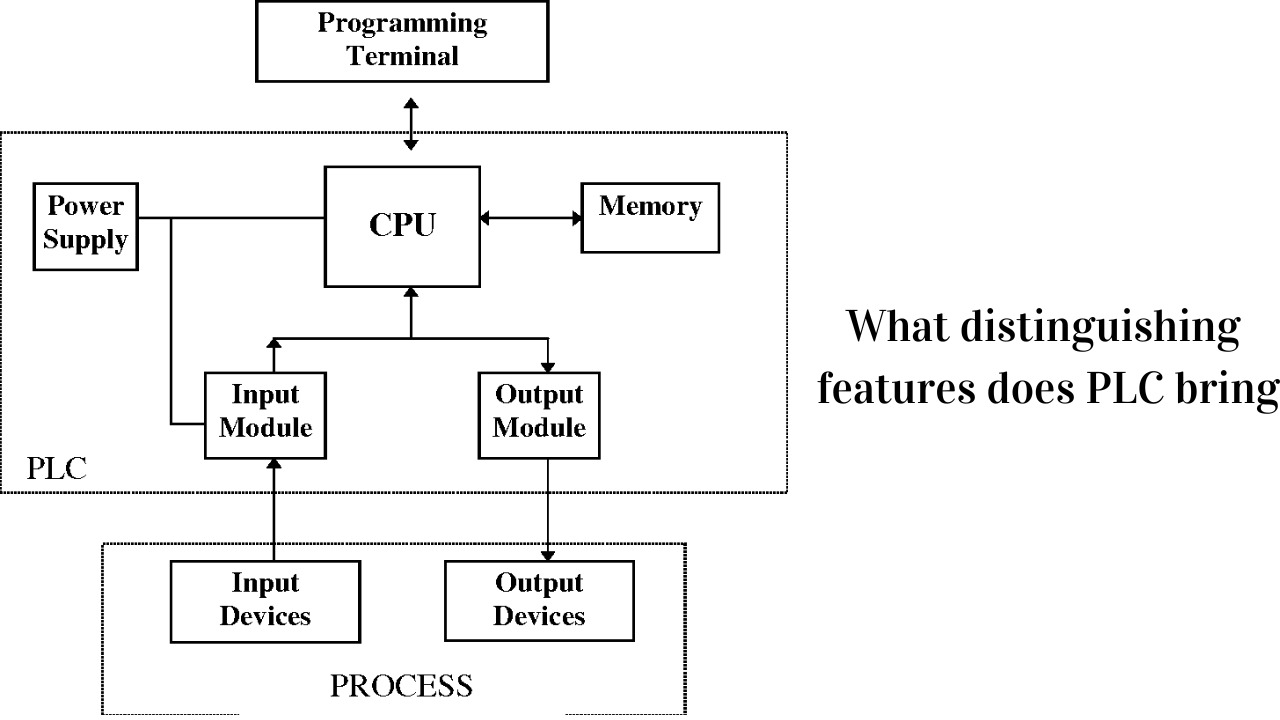
PLC, or programmable logic controller, is a specialized digital computer designed for industrial applications. It is used to automate processes and control machinery in manufacturing plants, factories, and other industrial settings. PLCs offer several distinguishing features that make them a preferred choice in industrial automation:
Durability:
PLCs are designed to operate in harsh industrial environments with extreme temperatures, vibration, and electromagnetic interference.
One of the main advantages PLCs offer industrial automation systems is durability. PLCs are built to perform consistently in challenging conditions, such as high humidity, vibration, dust, and temperature variations. They are designed with a long mean time between failure (MTBF) and high reliability to withstand the rigors of continuous operation. PLCs are thus a dependable and durable solution for managing crucial operations in industrial settings.
Programmability:
PLCs are programmable and can be customized to meet the specific needs of the application.
One of the primary characteristics that set PLCs apart is their ability to be programmed. A number of programming languages, including ladder logic, structured text, function block diagrams, and sequential function charts, can be used to program PLCs. As a result, engineers and technicians can create tailored software to satisfy the particular needs of a particular industrial automation application. PLCs are also highly adaptable to changes in production processes or new product designs because they can be reprogrammed as required.
Flexibility:
PLCs can be easily reprogrammed or reconfigured without the need for extensive rewiring or modifications to the system.
Flexibility is one of the distinguishing features of PLCs. They can be easily reprogrammed to perform different tasks, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. PLCs can be used in various industrial sectors, including manufacturing, automotive, and food processing, among others. Additionally, they can be customized to meet specific application requirements, allowing for a more efficient and effective operation of the system. This flexibility also enables PLCs to adapt to changing industrial needs, such as new production processes or increased demand.
Real-time operation:
PLCs operate in real-time, providing accurate and timely control of industrial processes.
Real-time operation is a distinguishing feature of PLCs that allows them to perform control functions with extreme precision and speed. PLCs are designed to operate in real-time, meaning that they can process input signals, execute control logic, and produce output signals in a matter of milliseconds. This is essential for applications where timing is critical, such as in manufacturing processes that require precise synchronization of multiple machines and sensors. With real-time operation, PLCs can respond to changes in the system instantly, ensuring that the process runs smoothly and efficiently.
Safety:
PLCs are designed with built-in safety features to protect workers and equipment.
PLCs have built-in safety features, such as emergency stop circuits, redundant systems, and fault detection, to ensure safe and reliable operation of machinery and equipment. They are designed to meet industry standards for safety, such as the ISO 13849 and IEC 62061 standards, and can be programmed to perform safety functions like monitoring and controlling safety-critical processes. This makes PLCs an essential component of safety-critical systems in industries like manufacturing, oil and gas, and transportation.
Communication:
PLCs can communicate with other devices, such as sensors, actuators, and other PLCs, allowing for coordinated control of complex processes.
PLCs come with various communication capabilities that enable them to communicate with other devices and systems within the industrial automation network. They can exchange data with sensors, actuators, human-machine interfaces (HMIs), supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, and other PLCs. Communication can be established using various protocols, including Ethernet/IP, Modbus, Profibus, Profinet, DeviceNet, and many others. This communication allows for real-time monitoring, control, and analysis of industrial processes and enables the integration of multiple systems and devices into a single control system.
Scalability:
PLCs are scalable and can be used in small or large-scale applications.
Scalability is a distinguishing feature of PLCs that refers to the ability to expand or reduce the size of the control system according to the changing needs of the industrial process. PLCs can be easily scaled up or down by adding or removing input/output modules, communication modules, or even CPUs. This allows industrial plants to adapt to changing production needs and expand their operations without requiring a complete overhaul of the control system. Additionally, with the use of networked PLCs, multiple PLCs can be connected and synchronized to manage complex production lines, making the system more scalable and flexible.
Overall, PLCs offer a reliable, flexible, and efficient solution for industrial automation and control.